Public sewer
|
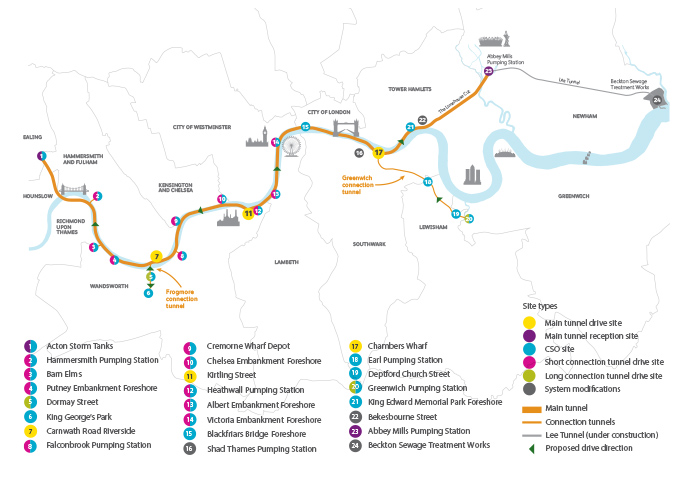
| The Thames tideway tunnel comprises a 24km long 7.2m diameter sewer running from Acton in the west to Abbey Mills in the east. It will have a holding storage capacity of 1.6 million cubic metres. |
A pipe that serves only one property is referred to as a drain. Drains are privately owned and maintained as far as the boundary of the property. Beyond the boundary of the property a drain is referred to as a public lateral drain.
A pipe that serves more than one property is referred to as a sewer. Sewers that connect to the public sewer network are referred to as public sewers.
The sewer system, that is, the underground network of pipes that carries sewage (waste water and excrement), other waste water and surface water run-off, from properties to treatment facilities or other disposal points is referred to as sewerage.
Under the Public Health Act 1936 all sewers (as defined by the Public Health Act 1875) which were in existence on 1 October 1937 became public sewers. After 1937 new sewers were only public if they were laid or adopted by the sewerage undertaker.
However, on 1 October 2011 in England and Wales, private sewers and lateral drains that were connected to the public sewer before 1 July 2011 were transferred to the ownership of the regulated sewerage companies (generally water companies).
It is possible to apply for new or existing sewers or lateral drains to be adopted by a sewerage company. For more information see:
Public sewers usually run under roads or public open spaces, but they may also run through private property such as gardens. The sewerage company has a right of access to these public sewers in order to maintain them.
Permission is required from the sewerage company to build over a public sewer. Failure to obtain permission may result in the withholding of a building regulations completion certificate.
It is also possible to have public sewers diverted under Section 185 of the Water Industry Act.
The route of existing mapped public sewers can be determined by inspecting local authority records or by contacting the local sewerage company. There may also be details in property deeds. However, many public sewers are not mapped. In this case, it may be necessary to carry out inspections from manholes, to undertake an electronic sewer trace or to dig trial holes.
- A surface water drain or sewer is a pipe that carries only surface water, not foul water.
- A foul water drain or sewer is a pipe that carries waste water from a property such as from a toilet, bath, washing machine and so on. Surface water should not discharge into a foul water drain or sewer, as this can cause flooding of foul water.
- A rising main is a pressurised sewer that can be used to pump foul or surface water.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Cesspool.
- Clarified water.
- Difference between drains and sewers.
- Drainage.
- Drains.
- Grease management.
- Manhole.
- Private sewer.
- Public Health Act 1875.
- Safe working in drains and sewers.
- Sanitary pipework.
- Section 102 existing sewer adoption.
- Section 104 new sewer adoption.
- Septic tank.
- Sewer construction.
- Sewerage.
- Sewerage company.
- Sustainable urban drainage systems SUDS.
- Thames Tideway Tunnel.
- The redevelopment of Leicester's sewerage system by Joseph Gordon.
- Waste water.
Featured articles and news
Amendment to the GB Energy Bill welcomed by ECA
Move prevents nationally-owned energy company from investing in solar panels produced by modern slavery.
Gregor Harvie argues that AI is state-sanctioned theft of IP.
Heat pumps, vehicle chargers and heating appliances must be sold with smart functionality.
Experimental AI housing target help for councils
Experimental AI could help councils meet housing targets by digitising records.
New-style degrees set for reformed ARB accreditation
Following the ARB Tomorrow's Architects competency outcomes for Architects.
BSRIA Occupant Wellbeing survey BOW
Occupant satisfaction and wellbeing tool inc. physical environment, indoor facilities, functionality and accessibility.
Preserving, waterproofing and decorating buildings.
Many resources for visitors aswell as new features for members.
Using technology to empower communities
The Community data platform; capturing the DNA of a place and fostering participation, for better design.
Heat pump and wind turbine sound calculations for PDRs
MCS publish updated sound calculation standards for permitted development installations.
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
























